Keto vs. Paleo: How Do These Popular Diets Compare?

Keto and paleo are two of the most popular diets in recent times.
For the past decade, paleo diets have been number one.
Over the past year or so, the tide has been turning, and the popularity of ketogenic diets is now surging.
This article will provide a balanced look at the fundamental differences, benefits, and drawbacks of keto vs. paleo.
A Brief Summary of Both Diets
Here is a look at the history of keto and paleo diets and how they have changed throughout the years.
Keto
Ketogenic diets restrict dietary carbohydrates to a maximum of 50 grams per day, but many followers consume much less.
Instead of carbohydrate, fat is the primary macronutrient, alongside a moderate protein intake.
The first reference to a ketogenic diet came in 1921 from Russel Wilder at the Mayo Clinic. Notably, he discovered the diet could successfully treat epilepsy patients, and he conducted successful clinical trials during the same year (1).
Since this time, the high-fat plan has been a fringe-diet that has mainly been in use for medical purposes. For example, it has primarily been a treatment for epilepsy, and it has become increasingly popular as a dietary option for type 2 diabetes.
The Atkins and Paleo diets of the nineties and noughties contained elements of the ketogenic diet, but they were more lenient in their carbohydrate allowance.
Recently, keto has gained mainstream popularity as a weight loss diet and for general health.
Paleo
Paleo, otherwise known as the paleolithic diet, refers to a way of eating that aims to replicate typical diets of the paleolithic era.
The paleolithic era took place from approximately 2.5 million years ago, and finished around 10,000 BC, around the time of the agricultural revolution.
In other words, the paleo diet allows you to eat anything a caveman could hunt or gather.
On the other hand, followers of the diet should avoid anything that only became possible with agriculture, with grains being a prime example.
The first advocate of the paleo diet was Dr. Walter L. Voegtlin, who wrote a book entitled ‘The Stone Age Diet’ in 1975. However, the diet didn’t become a mainstream trend until the release of ‘The Paleo Diet’ by Dr. Loren Cordain in 2002.
What is the Difference Between Keto vs Paleo?

There are a few similarities between keto and paleo diets, but there are also some significant differences.
Let’s first take a look at how the diets are similar, before looking at how they are different.
Similarities
- Both diets emphasize natural, whole foods.
- Neither paleo nor keto diets restrict dietary fat.
- Paleo and ketogenic diets both feature moderate to high protein from animal foods.
- Followers of both diets restrict foods such as processed vegetable oils, grains, legumes and other refined carbs/sugars.
- It is possible to follow both diets simultaneously, i.e. a paleo diet that encourages nutritional ketosis. In other words, a low-carb, high-fat paleo diet.
Differences
- Paleo diets are not necessarily low in carbohydrate and often feature high-sugar fruits and starchy carbs. In contrast, sufficient carb restriction to enter nutritional ketosis is the main focus of ketogenic diets.
- To expand on the previous point, the overall macronutrient profile is very important for ketogenic diets. For instance, carbohydrate should be 5-10% (maximum) of total energy intake. Paleo is more concerned about whether food could be naturally eaten in the paleolithic era, whether carbohydrate, fat or protein.
- Dairy products such as cheese, cream, and yogurt are perfectly fine for ketogenic diets, and positively encouraged. However, paleo shuns dairy foods.
Keto vs Paleo: Allowable Foods
The table below provides an at-a-glance summary of which foods are encouraged (and restricted) on both diets.
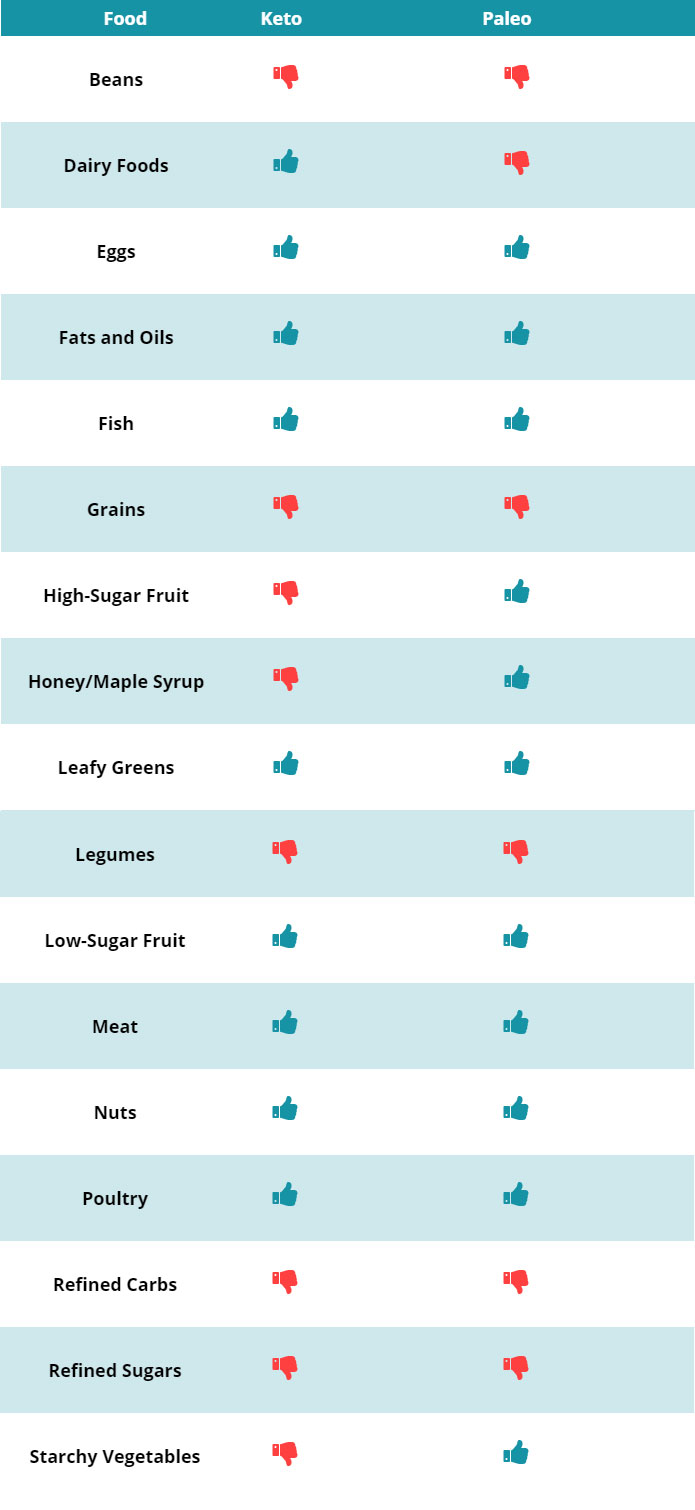
Beans
Beans only became available with the advent of agriculture, and they are relatively high in carbohydrate. Hence, both diets restrict them.
Dairy Foods
Dairy was not a part of the paleolithic diet, and so the paleo diet restricts all types of dairy foods (2).
On the other hand, ketogenic diets positively encourage high-fat dairy consumption.
However, care should be given with milk since it is reasonably high in carbohydrate at 5 grams per 100 ml.
Eggs
Eggs are a low-carb, high-fat food that has been part of the human diet for millions of years. As a result, they are suitable for both keto and paleo diets.

Fats and Oils
Healthy fats and cooking oils are allowable foods on both diets, although we should focus on natural fats rather than industrially processed ones.
In other words; animal fats, avocado, coconut, and olive oil are fine, but no trans-fats and ultra-processed vegetable oils.
Fish
Fish are one of the healthiest foods in the world, and they are a good choice for ketogenic and paleolithic plans.
Oily fish are especially beneficial due to their omega-3 content. For example; anchovies, herring, mackerel, salmon, and trout.
Grains
It only became possible for humans to eat grains (in mass) with the advent of agriculture, and so they are not a paleo-friendly food.
Cereal grains are also very high in digestible carbohydrate, making them a poor choice for keto diets.
High-Sugar Fruit
Higher sugar fruits such as grapes, mangoes, and papayas are natural foods that humans have eaten for a long time. While they may not be the same nutritionally as they once were, these foods are generally accepted as ‘paleo’.
However, such fruits are too high in carbohydrate to be compatible with ketogenic diets.
 Honey/Maple Syrup
Honey/Maple Syrup
Humans have been dodging angry bees to get at their honey for a long time. Since honey and maple syrup are natural sugars, they are OK for paleo diets.
Although they are natural, they are still concentrated sources of sugar, so they are not keto-friendly.
Leafy Greens
Leafy green vegetables are incredibly nutrient-dense and very low in carbohydrates.
They have also been part of the human diet for millennia, and they accordingly play a role in both keto and paleo.
Legumes
Although some legumes such as lentils are relatively nutrient-dense, they are too high in carbs to be considered a keto food.
Additionally, they are not considered to be a paleo food.
Low-Sugar Fruits
Low-sugar fruits such as avocados, berries, and olives are perfectly acceptable for a keto diet.
Humans have been picking fruit as far back as history goes, so they are an excellent option for paleo diets too
Meat
Humans living in the paleolithic era are commonly known as ‘hunter gatherers’ and meat was always a prized commodity.
Meat is also a perfect food for a keto diet; it is full of beneficial nutrients and contains zero carbohydrate.
Nuts
Nuts are perfectly compatible with ketogenic and paleo diets.
All types of nuts are no problem, but people following a ketogenic diet may wish to limit certain nuts.
In particular, cashews and pistachio nuts contain 30 grams and 28 grams of carbs per 100 g respectively (3, 4).
Poultry
Chicken, duck, turkey and other types of poultry are suitable for both diets.
On a ketogenic diet, fattier cuts are ideal.
Refined Carbs and Sugars
Since they are industrially manufactured and loaded with sugars/starch, refined carbs and sugars are a no-go on keto and paleo.
Starchy Vegetables
High-carbohydrate veggies such as parsnips, potatoes and sweet potatoes do not fit with the aims of a ketogenic diet.
However, they are encouraged on a paleo diet.
See this shopping list for ketogenic dieters for more information on suitable foods for keto.

Which Diet is Best For Weight Loss?
People often wonder how a particular diet compares to others concerning weight loss.
However, it depends on whether the specific diet is right for you.
For example, if someone doesn’t really buy into a particular diet, then they are unlikely to adhere to it.
Keto
Ketogenic diets may potentially help with weight loss in the context that people stick with the diet.
For example, some studies show that in ketogenic weight loss interventions, participants experience better appetite regulation and improved satiety levels (5, 6).
This is one of the most significant advantages of keto diets. Struggling to lose weight while simultaneously fighting hunger is one of the hardest things about weight loss.
On the negative side, the ketogenic diet is notoriously difficult to start.
For many people, entirely giving up on all sources of starchy carbohydrates is unimaginable, and some find it difficult to restrict carbohydrate to such low levels.
Success with keto very much depends on researching the diet, and properly committing and adhering to it.
For example, there is a myth that ketogenic diets virtually guarantee weight loss, but this is far from the truth.
For those who understand what the diet entails and are willing to give the diet a shot, ketogenic diets often have dramatic weight loss results.
Paleo
Similar to any diet, a well-implemented paleo diet can lead to weight loss when done well.
However, unlike low-carb and ketogenic diets, there is very little research on paleo diets being used as health interventions.
Probably the best study is a systematic review from 2015 that analyzed four randomized, controlled trials with a total of 159 participants.
The results of this study demonstrated that participants following a paleolithic diet reduced their weight circumference. Additionally, over a short-term duration of 2 – 28 weeks, participants experienced statistically significant weight loss (7).
What Are the Health Benefits of Keto and Paleo?
Paleo

Generally speaking, people view paleo diets as a way of adopting an overall healthy lifestyle.
However, studies do show they have specific benefits too.
For one thing, randomized trials show that they can improve glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors.
Interestingly, in one randomized trial, paleo diets outperformed a typical diabetes diet for controlling type 2 diabetes (8, 9).
A randomized trial also compared a paleo diet to the Australian Guide For Healthy Eating’s diet. Notably, the paleo diet had a larger impact on improving body composition, with no significant differences in other health markers (10).
Keto
In contrast to paleo, people often turn to keto diets as a health intervention, particularly for help with weight loss or type 2 diabetes (11, 12).
Since ketogenic diets improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fasting blood-glucose, they can be especially useful for those with some degree of insulin resistance.
Typically, ketogenic diets also increase levels of HDL while lowering triglycerides.
This health marker is an important factor, as studies show a high ratio of triglycerides to HDL has a strong association with the extent of cardiovascular disease (13).

Which is More Sustainable?
Sometimes people struggle to stick with their diet…
The merits of a particular diet often depend on how easily people can adhere to it.
Unfortunately, there are no studies that directly compare these two diets in this regard, so the answer is debatable.
My personal opinions;
- Given the initial side effects ketogenic diets can have, paleo diets are easier to adhere to in the first week or two.
- Many people on ketogenic diets find that their cravings for sweet foods quickly dissipate. In this respect, a diet that can minimize food cravings is one that can encourage adherence.
- Paleo diets give an overall wider choice of foods, which may be an important factor for some people.
- Both diets tend to be higher in protein than the average carb-heavy standard Western diets. As protein is the most satiating macronutrient, both diets are likely to improve appetite regulation (10).
- Food preferences will likely play a role in adherence; is a higher fat intake and a diet containing dairy foods ideal? Or is there a preference for a diet containing starchy vegetables and fruits?
Keto vs Paleo: Which Is the Better Choice?
Both diets are a big improvement on the heavily processed foods most people subsist on.
While carbohydrate restriction is not necessary for everyone, many people find success and improve their heath with keto diets, which is great.
On the other hand, for those who are otherwise healthy, a paleo diet containing more fruit and veggies may be the preference.
It essentially comes down to what you prefer; more fruits and starchy carbohydrates?
Or more steak, cheese, and avocados?
For more comparisons, see this guide to low carb vs keto.

 Honey/Maple Syrup
Honey/Maple Syrup
7 thoughts on “Keto vs. Paleo: How Do These Popular Diets Compare?”
very informative article thank you
Thanks, Josephine.
Glad it helped!
Very informative but, understandably – yet disappointing, you ‘sit on the fence’. I am 63 and have lived an incredibly unhealthy life style for most of that time. My diet consisted of mostly processed foods, full of carbs.
My favourite foods were staples such as potatoes, breads and cereals. I started reading about diets when my health deteriorated, as i knew it surely would at my age.
Suddenly (or more accurately, over the past 30 years) i find i am pre-diabetic, i have had prostate surgery and am grossly overweight. My cholesterol is high and I have CMT Type 1 – a genetic nerve disorder of which i have no control.
I began researching diets just after Christmas of 2017, knowing i had to do something. From all my readings – and there were many – i narrowed it down to either Paleo or Keto. The deciding factor for me came down to the fact that i knew two people already on one of the diets and both were highly convinced it was the best thing ever.
So on January 20, 2018 I began my KETO journey. At no stage did i find it difficult to switch. This diet made more sense due to its stance on carbs and sugars. The result so far – Jan 20 I weighed 124.7kgs, today – March 17 i weigh in at 111.1kgs – a difference of 13.6kgs in almost 8 weeks. I have a way to go to reach my goal weight of 80kgs but i am well on the way and it will be KETO all the way for me! Key things to watch out for – the KETO flu – it is real, but easily overcome. Also constipation (or the opposite) can affect some people – it did me. Again, easily controlable. I urge those on any diet to get their bloods checked regularly and be guided by the results – mine have never been better! Oh, and by the way – i have never felt better mentally than i presently do. KETO can be expensive with all the ingredients need to stock your pantries, but the one single thing that i think assists weight loss the most is FREE. WATER! drink lots of water and keep hydrated if doing the KETO WOE
Hi Tony,
Firstly, well done on your great progress so far!
Thanks for the insightful feedback and information.
Glad you found it informative, and I also understand why you found the “sitting on the fence” disappointing. I always feel like that whenever I read a “something vs something” article too!
Personally, I’m a believer in the health benefits of low-carb and keto diets (as you can probably tell from many of the articles covering them!) However, we have to understand that people have different needs and desires, have different health concerns, etc.
Calling one diet the best for someone who clearly has no intention of following the restrictions can be unhelpful, and anyone involved in nutrition/dietetics has to consider this.
For anyone in your situation, i.e. someone who found they had pre-diabetes and wished to lose weight, then understandably a ketogenic diet would be far better than a paleo diet. And that’s based on the wealth of current science.
Keto diets beat any other in that regard, as evidenced by systematic reviews of RCTs.
What diet would be best for fatty liver?
Sorry, I don’t have enough knowledge on fatty liver to comment. I would really recommend speaking to your doctor for accurate and personalized advice.
Keto podcast alway say to eat that.
Comments are closed.