5 Nutrition Benefits of Ricotta Cheese (and How To Use It)
Ricotta is one of the most famous cheese varieties, and it is especially popular in the United States and its homeland of Italy.
This article looks at precisely what ricotta cheese is, the nutrition profile, potential health benefits, and how to use it.
What Is Ricotta?
Ricotta is a fresh cheese from Italy with a soft and creamy taste, and it is has a long history that predates even Roman times.
The literal English translation of ricotta is “recooked,” and this refers to the way the cheese is made.
The production of ricotta is very different from traditional cheese, and producers make it by “recooking” leftover liquids from cheesemaking.
Researchers believe the cheese first became popular way back in the Bronze age (1).
How Is It Made?
At first glance, ricotta looks strikingly similar to cottage cheese.
However, since ricotta has a very different production process, that is where the similarities end.
Traditional Style Ricotta
Interestingly, traditional-style ricotta is a byproduct of the cheesemaking process.
Producers make this ricotta by heating and coagulating the leftover whey proteins following the production of other types of cheese such as mozzarella.
After this, they add small amounts of milk.
Modern Ricotta
In recent times, fresh ricotta made with whole milk has gained popularity.
Although similar in taste, this version has a different production method and it is slightly creamier.
To make modern-style ricotta, the producers use fresh whole milk rather than leftover liquid whey.
Taste
Ricotta cheese has a mildly sweet taste, and it is also slightly salty. Although the texture is thick and lumpy, it tastes reasonably smooth.
For those who haven’t tried it before, ricotta is perhaps closest to feta cheese in taste and texture.
Nutrition Facts
The tables below show the full nutrition profile for ricotta cheese per 100 grams (2).
| Calories/Nutrient | Amount (kcal/grams) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 174 kcal |
| Carbohydrate | 3.0 g |
| Fiber | 0 g |
| Sugar | 2 g |
| Fat | 13.0 g |
| Saturated Fat | 8.3 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 3.6 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0.4 g |
| Omega-3 | 112 mg |
| Omega-6 | 273 mg |
| Protein | 11.3 g |
As shown in the table, ricotta provides a large amount of fat and protein, and a small amount of carbohydrate.
| Vitamin | Amount (% RDI) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B2 | 11 % |
| Vitamin A | 9 % |
| Vitamin B12 | 6 % |
| Folate | 3 % |
| Vitamin B5 | 2 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 2 % |
| Vitamin E | 1 % |
| Vitamin K | 1 % |
| Vitamin B1 | 1 % |
| Vitamin B3 | 1 % |
Ricotta contains a decent amount of vitamin A and B2, as well as small amounts of most other vitamins.
| Mineral | Amount (% RDI) |
|---|---|
| Calcium | 21 % |
| Selenium | 21 % |
| Phosphorus | 16 % |
| Zinc | 8 % |
| Potassium | 3 % |
| Magnesium | 3 % |
| Sodium | 3 % |
| Iron | 2 % |
| Copper | 1 % |
Ricotta is an excellent source of calcium, selenium, and phosphorus. It also contains lower amounts of numerous other essential minerals.
Benefits of Ricotta Cheese
Here are some of the main benefits that ricotta cheese offers.
1) Rich In Protein
Ricotta is a good source of protein, and it contains 11.3 grams per 100 g, which works out to be 11.3 grams per 173 calories.
For anyone looking to emphasize protein density, low-fat ricotta offers an even better amount of protein per calorie.
Per 100 grams, low-fat ricotta provides 11.4 grams of protein for only 138 calories (3).
As a source of dairy, the protein content of ricotta is a ‘complete protein,’ meaning that it contains all the essential amino acids in adequate amounts (4).
Protein is important for building and maintaining muscle, manufacturing enzymes and hormones, and it plays a role in keeping bones, skin, hair, and nails healthy (5).
2) Supplies DHA and EPA Omega-3
Since ricotta usually comes from animals raised on pasture, it provides a good amount of omega-3 in its DHA/EPA form.
Unlike plant foods such as nuts and seeds, DHA and EPA is the same form as omega-3 found in oily fish and seafood.
In this regard, it is important to note that our body can use DHA and EPA omega-3 “as is” and it doesn’t require converting to anything else (6).
Before our body can use the ALA (plant) form of omega-3, we need to convert it to DHA and EPA inside the body, and this conversion rate can be as low as 0% to 21% (7).
Omega-3 has several beneficial effects on our health, and these include its ability to lower triglycerides and raise HDL levels. Additionally, it may also have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity (8, 9, 10).
While all kinds of ricotta will provide omega-3, the amount will be higher in ricotta made from milk by animals raised on pasture.
3) High In Selenium
Selenium is an important antioxidant mineral, and it plays a role in protecting the body from free radical damage and oxidative stress (11).
Unfortunately, approximately one in seven people around the world have an inadequate dietary intake of the mineral. Researchers also expect this number to increase since soil concentrations of selenium appear to be decreasing (12).
On the positive side, ricotta is a good source of this essential mineral. One hundred grams of ricotta cheese provides over 20% of the RDI (2).
4) A Good Source of Calcium
The second mineral that ricotta provides in reasonably large amounts is calcium.
Calcium is one of the major nutrients in all milk and cheese products, and ricotta is no different.
Specifically, one serving of ricotta supplies more than one-fifth of the daily RDI for calcium (2).
Calcium has several important functions in the body, and it is particularly important for maintaining healthy bones, nerve signaling, and muscle function (13, 14).
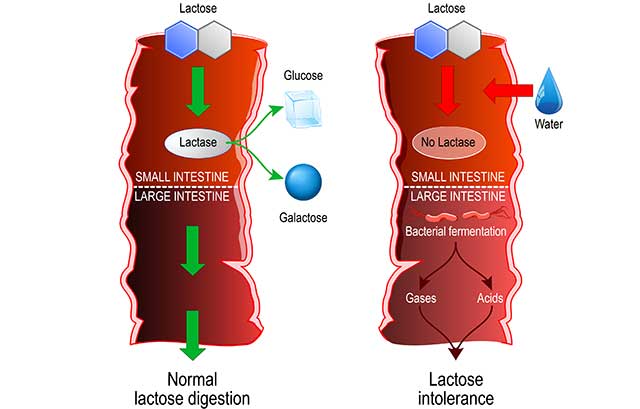
5) Lower In Lactose Than Some Dairy Products
Lactose intolerance and sensitivities are common around the world.
While lactose issues are rare in individuals with Northern European ancestry, more than 90% of people have lactose intolerance in parts of East Asia (15).
Lactose intolerance can cause frustrating symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, cramps, and diarrhea (16).
Ricotta cheese comes under the ‘low lactose’ category of dairy foods, and it contains around two grams of lactose per 100 g (17).
This amount of lactose is much lower than in foods like milk and yogurt, and it may make ricotta tolerable to people with slight lactose sensitivities.
However, for people with strong reactions to lactose ingestion, this is still likely too much lactose.
Potential Drawbacks
While ricotta is a healthy dairy food that provides several benefits, it may cause issues for certain groups of people.
Similar to most dairy products, people with severe lactose intolerance may wish to avoid ricotta cheese.
Ricotta will also cause problems for anyone with a whey protein allergy.
However, it does not contain casein protein.
How To Use Ricotta Cheese
Ricotta is easy to use and very versatile, but it isn’t quite the same as harder varieties of cheese.
To put it another way; this cheese isn’t something you’ll see on wine platters or in sandwiches.
Here are some tasty ways to use ricotta.
- Omelets: Put a little ricotta inside a meat-based omelet for a creamy, cheesy filling.
- With berries: For a quick and simple dessert (or healthy snack) mix your favorite berries into a bowl of ricotta.
- Dip: ricotta makes a great dip; just add some black pepper, salt, finely diced onions, and chives.
- Scrambled eggs: For truly delicious scrambled eggs, try making them with ricotta. All you have to do is beat some ricotta with your eggs in a bowl, add salt and pepper, and then cook the mixture in a bit of butter.
There are all kinds of ways to use ricotta, and it can work well as an addition to almost any dish.
Even putting it in soups and stews can upgrade the overall flavor, so experimenting with new recipes is a great idea too.
Final Thoughts
Overall, ricotta cheese is a healthy and delicious-tasting cheese.
It is high in protein, contains several important nutrients, and it can add a great deal of flavor to our food.
Related Articles
19 Types of Cheese: Delicious and Nutritious Options
Is Cottage Cheese Healthy? (and Full Nutrition Facts)